Third, the purification of leachate 2FeWO4+2CaO+1/2O2 =2CaWO4+Fe2O3 The sodium tungstate solution obtained by the above various methods for decomposing the low-grade tungsten mineral raw material contains impurities such as silicon, phosphorus, arsenic, and copper to various degrees, and sometimes contains impurities such as sulfur and fluorine. In order to ensure the quality of the chemical concentrate, the leachate must be purified to remove impurities. The following methods are commonly used at present. 1. Remove silicon, phosphorus and arsenic with ammonium magnesium salt. Silicon should be removed when the weight ratio of SiO2 / WO3 in the immersion liquid is greater than 0.1%. Silicon is present in the solution in the presence of sodium silicate, and when the alkalinity of the solution is lowered, the hydrolysis is precipitated as silicic acid. Therefore, adding 1:3 dilute hydrochloric acid to the immersion liquid to lower the pH to 13, then adding ammonium chloride to lower the pH to 8-9, sodium silicate can be completely hydrolyzed to form SiO2 precipitate, and then clarified and filtered. After washing, the silicon oxide in the liquid can be reduced to 0.25 g/l. Phosphorus arsenic exists in the form of HPO42- and HAsO42- in the silicon removal solution, and a magnesium oxide solution having a density of 1.16.18.18 g/cm 3 is added thereto at room temperature, and the phosphorus and arsenic are respectively ammonium magnesium phosphate Mg (NH4). The form of PO4 and ammonium magnesium arsenate Mg(NH4)AsO4 precipitated. 2. Magnesium salt method removes silicon, phosphorus and arsenic. In this method, the pH value of the immersion liquid is reduced to less than 11 by dilute hydrochloric acid (1:3), and the sodium silicate is partially hydrolyzed. At this time, the phosphorus in the immersion liquid is in the form of HPO42- and arsenic in the form of HAsO42-. When a density of 1.6-1.18 g/cm 3 of magnesium chloride solution is added until the alkalinity of the immersion liquid is 0.2-0.3 g / liter of NaOH, precipitates of MgSiO3, Mg3(PO4)2, and Mg3(AsO4)2 are precipitated, so that magnesium chloride may be added. Remove silicon, phosphorus, and arsenic. The main point of this method is to neutralize the immersion liquid to pH 11 with hydrochloric acid and then add the magnesium chloride solution, otherwise magnesium hydroxide precipitation will occur. When the content of the fluorite in the raw material is large, magnesium chloride may be added to precipitate the F- in the immersion liquid as MgF2. The ammonium magnesium salt method and the magnesium salt method can only remove high-priced arsenic. If low-cost arsenic is present, the low-priced arsenic must be oxidized to high-priced arsenic with an oxidizing agent such as hydrogen peroxide or sodium hypochlorite, and then magnesium oxide can be added to achieve the purpose of removing arsenic. The magnesium salt method has higher efficiency than the ammonium magnesium salt method, large processing capacity, short production cycle, and low slag containing tungsten (about 4-5% WO3), but the amount of slag is large. The amount of ammonium magnesium salt slag is small, but the slag contains high tungsten (about 15-20% WO3), so the best purification method should be determined according to the characteristics of the raw materials. 3. Alkaline method to remove molybdenum . Molybdenum exists in the form of sodium molybdate in the immersion liquid. In the filtrate after removing silicon, phosphorus and arsenic, sodium sulfide solution is first added to convert molybdenum into thiomolybdate, and arsenic remaining in the solution is also converted into thioarsenic. The acid salt was then neutralized with hydrochloric acid until pH=8.5, at which time molybdenum and arsenic did not precipitate. Further, a calcium chloride solution is added, and tungsten is precipitated as calcium tungstate, and molybdenum and arsenic remain in the form of the corresponding thioacid salt, and the molybdenum and arsenic are removed by filtration. In addition to the molybdenum rate of 70-90%, the amount of sodium sulfide added is 8-8.5 times the total amount of molybdenum and arsenic, and the temperature is 80 degrees. When the amount of molybdenum contained in the immersion liquid is less than 0.25 g/L, it is not necessary to separately remove the molybdenum process, and the method for improving the acidity of decomposing and synthesizing scheelite achieves separation of tungsten and molybdenum, high acidity, high temperature and good molybdenum removal effect. There are other methods other than molybdenum, which are not described here. All of the above are chemical precipitation methods to remove impurities such as silicon, phosphorus, arsenic, and molybdenum in the immersion liquid, and other methods such as ion exchange.
PSA nitrogen generator and PSA Oxygen Generator have similar principle. Molecular sieve as an adsorbent under the principle of pressure swing adsorption (PSA), will get nitrogen/oxygen from compressed air.
Oxygen/Nitrogen/Argon Generation Plant/Gas Production Equipment Shenzhen KunPeng Precision Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.electronic-smt.com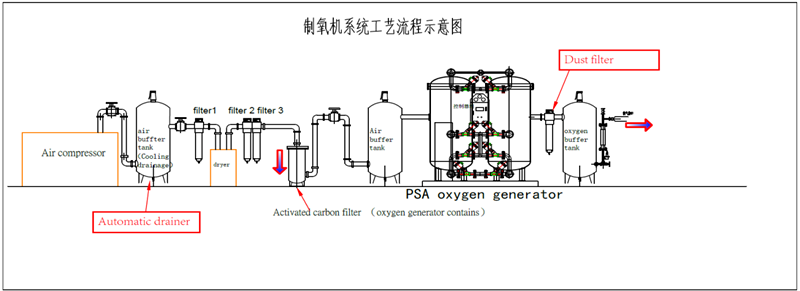
Two or three strokes of low-grade tungsten concentrate treatment purification leachate
The sodium tungstate solution obtained by the above various methods for decomposing the low-grade tungsten mineral raw material contains impurities such as silicon, phosphorus , arsenic and copper to various degrees. In order to ensure the quality of the chemical concentrate, the leachate must be purified to remove impurities. The following methods are commonly used at present. 1. Remove silicon, phosphorus and arsenic with ammonium magnesium salt . 2. Magnesium salt immersion method in addition to silicon, phosphorus, arsenic. .....