Woven Bag Hot-cutting Sewing Printing And Collecting Machine Woven Bag Hot-Cutting Sewing Printing And Collecting Machine Sewing Printing,Collecting Machine,Sewing Pattern Printer,Woven Bag Hot-Cutting Sewing Printing shandong Herui Mechanical Co., Ltd , https://www.heruihorsefloat.com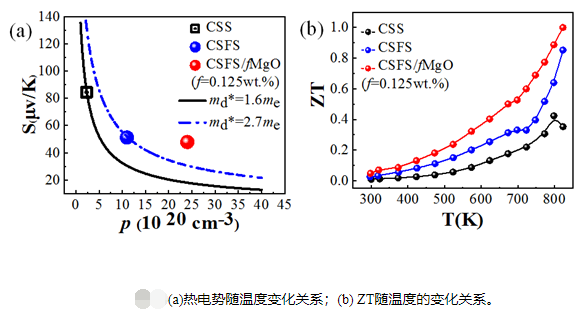
Thermoelectric technology is expected to solve energy problems, drawing attention to the progress of thermoelectric materials research
[ Instrument R & D of Instrument Network ] There are many types of energy, and after continuous development and research of human beings, more new energy sources have begun to meet human needs. With the acceleration of the global industrialization process, the world's energy shortage and depletion has become a problem that cannot be ignored by every country, which seriously restricts the long-term stable development of society. Research and development of new energy has become the trend of global energy development. There are a lot of thermal energy generated in life that is consumed by energy but discarded, for example: automobile exhaust gas, factory exhaust gas, etc.
It is understood that thermoelectric material is a functional material that can convert thermal energy and electrical energy. The Seebeck effect discovered in 1823 and the Peltier effect discovered in 1834 provide a theoretical basis for the application of thermoelectric energy converters and thermoelectric refrigeration. As interest in space exploration increases, advances in medical physics, and resource exploration and exploration activities that are difficult to increase on the planet, it is necessary to develop a type of power system that can supply energy without care, and thermoelectric power generation is particularly suitable for these applications.
Therefore, thermoelectric materials have attracted widespread attention in recent years as a new way to solve energy problems. Relevant scientific researchers are committed to this research and development. Recently, the research team of Qin Xiaoying, a research group of materials application technology laboratory of the Institute of Solids, Hefei Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made new progress in the regulation of thermoelectric properties of the Cu2SnSe3 material system. The researchers significantly improved the power factor of the material through energy band adjustment and energy filtering effect, and greatly reduced its lattice thermal conductivity, optimizing the thermoelectric performance of the material, so that the thermoelectric figure of merit of the material was increased to 1.
The conversion efficiency of thermoelectric materials is represented by the dimensionless quantity ZT, where ZT = S2σT / (κh + κL), where S is the thermoelectric potential, σ is the electrical conductivity, T is the absolute temperature, and κh and κL are the electronic thermal conductivity and lattice heat, respectively guide. Cu2SnSe3 (CSS) as an intrinsically low thermal conductivity environmentally friendly thermoelectric material has attracted wide attention, but due to its low thermoelectric potential and power factor (PF = S2σ), the quality factor of the material is restricted.
To this end, by adjusting the energy band structure by doping Fe at the Sn site, the researchers improved the degeneracy of the valence band top and the density of states near the Fermi level, which greatly increased the carrier mobility and effective mass of the CSS. This results in a significant increase in thermoelectric potential and power factor. At the same time, the researchers introduced MgO nanoparticles into Cu2Sn0.95Fe0.05Se3 (CSFS) to further increase the thermoelectric potential of the material through the energy filtering effect, and due to the interface scattering significantly reduced the lattice thermal conductivity of the material, making the ZT value increase at 823K By 1, it is 2.5 times higher than the base material.
About thermoelectric materials
Thermoelectric material is a kind of functional material that uses the movement of carriers in the solid to realize the direct conversion of thermal energy and electrical energy. People's understanding of thermoelectric materials has a long history. In 1823, the German Seebeck discovered that the temperature difference between the two ends of the material can produce a voltage, also known as the thermoelectric phenomenon. In 1834, the French watchmaker Peltier published a paper on the abnormal temperature difference that he observed near the boundary of two different conductors (when an electric current flows) in the French Yearbook of Physics and Chemistry. These two phenomena show that heat can call, and at the same time electricity can also be converted into heat or used for cooling. These two phenomena are named the Seebeck effect and the Peltier effect, respectively. They provide a theoretical basis for the application of thermoelectric energy converters and thermoelectric refrigeration. Nowadays, with the increasing environmental pollution and energy crisis, it is of great practical significance to conduct research on new thermoelectric materials.